Why in news?
Context- An Assam-based insurgent group-Dimasa National Liberation Army (DNLA)/Dimasa people’s Supreme Council (DPSC) – which operates in Dima Hasao district, signed a tripartite peace agreement with the state government and the Centre.
– The peace agreement envisages to setup Dimasa Welfare Council by Assam government to protect, preserve and promote a social, cultural, and linguistic identity to meet political, economic and
educational aspirations and will ensure speedy and focused development of the Dimasa people residing outside the Autonomous Council.
– The MoU also provides for the appointment of a Commission under Paragraph 14 of the Sixth Schedule to the constitution of India to examine the demand for the inclusion of additional villages
contiguous to the North Cachar Hills Autonomous Council (NCHAC) with the council.
– A special development package of rupees 500 crore each, will also be provided by the government of India and Government of Assam over a period of 5 years, for all-round development of NCHAC
and Dimasa people residing in other parts of the states.
– The agreement will put a complete end to insurgency and there are no more armed groups in Assam today.
– The agreement is another significant milestone towards making Northeast insurgency free by 2024.
– Other insurgency groups were active in Assam-ULFA (united liberation front of Assam), Bodo liberation tiger force, NDFB (national democratic front of Bodoland), Kamatpura liberation
organisation (KLO) etc.
About DNLA
– A new insurgent group formed in 2019 and was operating in Assam’s Dima Hasao and Karbi Anglong district.
– Slogan -committed to revamp the national struggle and fight for liberation of sovereign, independent Dimasa Nation.
– Aim -develop a sense of brotherhood among Dimasa people and also to rebuild the trust and faith among Dimasa society for regaining Dimasa kingdom.
– The group had run on a model of extortion and taxation and was believe to have drawn its support and sustenance NSCN(IM)- a insurgency group of Nagaland.
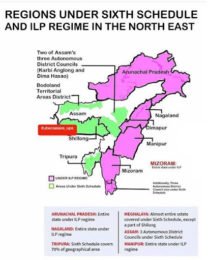
Constitutional safeguard to Tribal Group of Assam
– Under SIX schedule -constitution of district council and regional council.
– Art 244(2)-formation of an autonomous state comprising certain tribal areas in Assam.
– Art 275(1)-constitution of India guarantees Grant-in-Aids from the Consolidated Funds of India each year for promoting the welfare of the schedule tribe.
– Provision that allows for greater political autonomy and decentralised governance in tribal areas through formation of tribal autonomous council that are administer by elected
representative.
– The North Cachar Hill autonomous council, Dima Hasao, Karbi Anglong autonomous council, East Karbi Anglong are autonomous council constitute under the provision of six schedule of the
constitution to administer of respective district and for development of the tribal people.
Power of tribal autonomous district council
– Legislative and executive : Power covers subject like water, soil, land, local custom and culture.
Gives power to district council to make law for allotment, occupation, use of land other than reserve forest for purpose of agriculture, grazing etc. management of unreserved forest,
establishment of village council and town committee, administration of village policy, appointment of chief and headman of village, inheritance of property, money lending and trading by non-
tribal within the autonomous district. The governor has the power to alter the laws or rules passed by district council which violate the sixth schedule.
– Judicial : Power to settle certain types of civil and criminal cases. Council to constitute village and district council court in autonomous area to adjudicate or try case
or customary law in which both the parties are tribe and maximum sentence is less than 5 years.
– Financial : They have the responsibility for framing rules for the management of finance and approval of the Governor. The tax levy and collected mutually exclusive power of
regional council and district council. Royalty on licences or leases for the extraction of minerals in the autonomous district goes to district council. Tax on motor vehicles assigned and
collected by the state government om behalf of the district council.
Tribal district autonomous council in northeast






