Depleting Phosphorus: How Sewage become treasure
Concern: Deficiency of phosphorus in Indian Soil
- Phosphate rocks are found in Morocco, Western Sahara, China, the United States, Russia and West Asia. Therefore, India and other countries has to import it. In 2018, Diammonium phosphate constituted 28 per cent of India’s fertiliser import. Hence it concluded world will reach “peak phosphorus” in 2030.
“Peak phosphorus” — that point in time when production of phosphorus will reach its maximum and it will get harder to access it
- In Morocco and Sahara, here phosphorus core exist with cadmium (heavy metal), if that can accumulate in animal and human kidney when ingested removing cadmium is also an expensive process.
Hence it not easy to get phosphorus from such huge reserves.
- World’s reserve phosphorus owns by handful countries. It became a major Geo political concern.
- As a result, get me Laden fertilizers are of an applied to the soil absorbed by the crops and consumed bio-accumulating in our bodies.
There six countries have substantial cadmium free Phosphorus Reserve.
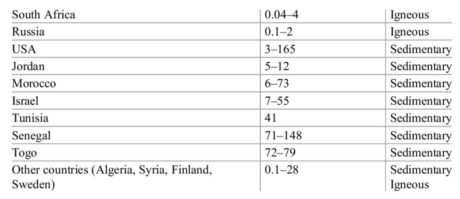
The link to join the course : Online Courses
- Of them China restricted export in 2020 and many EU countries no longer by from Russia so the market for safe Phosphorus has suddenly exploded.
- In 2021 Sri Lanka banned the import of synthetic Fertilizer and went organic, later experience a sudden drop in crop yield that that precipitated a political crisis.
- Today India is the world’s largest importer of phosphorus most of it from the cadmium Laden deposit of West Africa.
- Indian farmers use a lot of fertilizer to the crops like paddy so paddy a stable crop in India is particularly susceptible.
- Not all the crops absorb cadmium at the same rate, crops such as wheat Barley and maize also absorbed cadmium but comparatively very less
- The update of cadmium by crop varies based on the soil quality climatic conditions and the type and the variety of crops grown.

Social and cultural factors further affect the intake of cadmium into human body and the severity of health effects:
Issues with disposing Phosphorus:
- Only about a fifth of the phosphorus mined is actually consumed through food. Much of it is lost directly through water bodies as agricultural run-off due to the excessive application of.
- Most of the Phosphorus that people consume ends up in the sewage.
- It is then absorbed by the algal blooms that grow in response to the high nutrient supply, and when they decompose, the bacteria that feed on them consume the dissolved oxygen.
Hence water bodies become oxygen starved, leading to fish deaths.
- The algal blooms are also toxic, causing respiratory issues, nausea, and other ailments to people exposed to them.
Where to find Phosphorus?
- Recycling wastewater and sludge
- Finding phosphorus elsewhere Since much of the phosphorus is not actually taken up by crops, one way to ameliorate the phosphorus paucity is to reduce the use of chemical fertilisers through precision agriculture.
- There is increasing interest in closing the phosphorous loop by mining urban sewage to produce high quality phosphorus.
- Interest in ‘circular water economies’ has in fact prompted the European Union – which has almost no phosphorus reserves of its own – to rethink the urban water cycle.
The circular water economy is an innovative approach to water management that maximizes water resources, reduces waste and improves water resiliency through collaboration and innovative solutions for a sustainable future.
- First, source separating toilets – almost two thirds of the phosphorus we consume leaves in our urine and the rest in faeces. An important phosphorus resource from where a huge reserve can be generated has been largely ignored till now.
An analysis by Dutch non-profit WASTE shows India generates over 204 million tonnes of phosphorous per year.
The solid matter that humans excrete is largely organic. It contains carbon, phosphorous and a whole lot of other nutrients. Human consume these nutrients in the form of food. Leafy vegetables, for instance, have enormous phosphorus.
Best Online Coaching for Civil Service_IAS_ UPSC_IFS_IPS
Free Study Material ENSEMBLE IAS ACADEMY | Call +91 98115 06926 | Visit us:- https://ensembleias.com/ | Online Store: https://online.ensemble.net.in/
#Phosphorus #agriculture #soil_health #GSpaper3 #civil_services_study #ensemble_ias_academy #geography_optional #k_siddharthasir #ias #upsc_exam #civilservices #upsc_motivation #upsc_aspirants #trendsingeography




