GM Organism and GM crops :
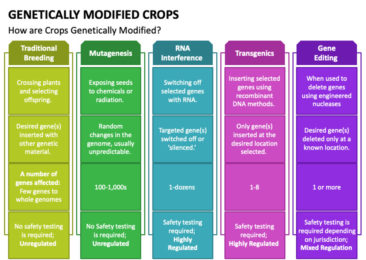
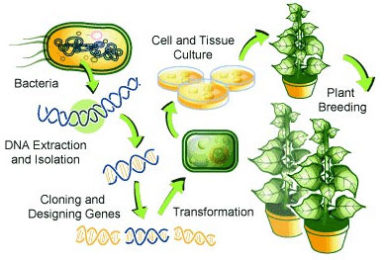
Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) can be defined as organisms (i.e. plants, animals or microorganisms) in which the genetic material (DNA) has been altered in a way that does not occur naturally by mating and/or natural recombination. The technology is often called “modern biotechnology” or “gene technology”, sometimes also “recombinant DNA technology” or “genetic engineering”. It allows selected individual genes to be transferred from one organism into another, also between nonrelated species. Foods produced from or using GM organisms are often referred to as GM foods.
The link to join the course : Online Courses
- In order to increase food production and become self-reliant, we require superior crop varieties and hybrids that provide enhanced yields and wide adaptability across environments, and require fewer inputs of natural resources
- Genetic modification of crops using the available and vast genetic diversity in conjunction with traditional farming has been well documented for increased productivity, contributing to global food, feed, and fibre security.
- According to a report by the International Service for the Acquisition of Agribiotech Applications (ISAAA) 2020, a total of 72 countries have adopted GM crops either as human food or animal feed, as well as for commercial cultivation (56% of the global GM crop area is in developing countries compared to 44% in industrial countries).
- GM crops have benefited more than 1.95 billion people in five countries (Argentina, Brazil, Canada, India and the United States) or 26% of the current world population of 7.6 billion.
- Globally, genetic modification has expanded its reach, beyond the major four crops, maize, soybean, cotton and canola, to other economically important food crops for various traits such as insect and herbicide resistance, climate resilience and nutritional quality improvement.
- In edible oil deficit, a focus on mustard India faces a major deficit in edible oils, with 60% of its demand being met by imports.
- Mustard is one of the most important edible oil crops in India; however, its per hectare yield is very low when compared to the global average.
- Thus, increasing the productivity of mustard in the country is
- vital for the economic wellbeing of farmers and self-sufficiency in edible oil production.
- Using genetic engineering, extensive research has been carried out at the Centre for Genetic Manipulation of Crop Plants (CGMCP), University of Delhi South Campus, to create a GM mustard hybrid, DMH11 with higher vigour and yield.
- This will facilitate an increase in domestic production of edible oils as well as enhanced farm incomes.
- The GM mustard hybrid is based on the barnase /barstar system, which works on the principle of removing male fertility in one parent and restoring it in the off-spring.
- The herbicide tolerance gene has been deployed as a selection marker for developing the GM mustard.
- While the use of herbicides in herbicide tolerant (HT) crops have an advantage in terms of saving soil moisture and nutrients, besides effective weed control, the herbicide tolerance gene in GM mustard is primarily used for selecting genetically transformed lines, and for hybrid seed production.
On October 25, 2022, the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change Government of India, made a landmark decision of approving the release of DMH11 and its parental line for cultivation.
- This will help boost the vibrant genetic engineering research sector in the country and enable the generation of new crop varieties with improved traits.
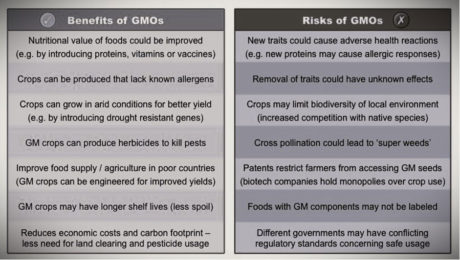
- The adoption of science-based technologies for crop improvement such as genetic engineering for developing genetically modified (GM) crops as a supplement to conventional breeding methods has become an absolute necessity to address the burgeoning and complex challenge of achieving global food and nutritional security under the fast-changing climate. According to the global Food Security and Nutrition Report, 2019, it is difficult to achieve the ‘Zero Hunger’ target by 2030.
Best Online Coaching for Civil Service_IAS_ UPSC_IFS_IPS
Free Study Material ENSEMBLE IAS ACADEMY | Call +91 98115 06926 | Visit us:- https://ensembleias.com/ | Online Store: https://online.ensemble.net.in/
#GM_Organism #GM_crops #GMOs #GM_foods #natural_resources #Zero_Hunger #groundwater #UPSC_GSPaper3 #GS_Paper_3 #civilservicesstudy #ensembleiasacademy #geographyoptional #k_siddharthasir #strategicthinker #ias #civilservices #upsc_motivation #upsc_aspirants #upsc_exam