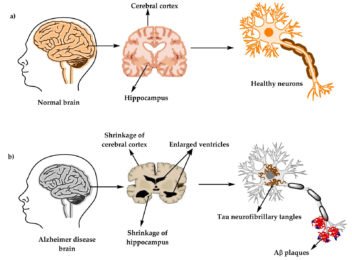
Alzheimer-21st Sept World Alzheimer’s Day
Emil Kraepelin (1856–1926), a doctor in Germany who classified dementia into senile dementia and presenile dementia in 1910 and Alois Alzheimer (1864–1915), who discovered pathological features of presenile dementia while his student.
Alzheimer, It is kind of disorder in a brain that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills and the ability to carry out the simplest tasks.
Alzheimer’s disease found Protein misfolding disease
Proteins can only carry out their various biological functions when they are rightly folded. Their amino acid sequence encodes the relevant information required for correct three-dimensional folding, with or without the assistance of chaperones. The challenge are linked with understanding protein folding is currently one of the most important aspects of the biological sciences. Misfolded protein intermediates form large polymers of unwanted aggregates and are involved in the pathogenesis of many human diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease.
The identification of several diseases as protein folding disorders can be found
- The explosion of genome information and the need for efficient ways to predict protein structure, protein folding has been projected as a fundamental issue in molecular sciences research
- To unfold the protein in high concentration of a chemical denaturant and then to dilute the solution so rapidly such that the denaturant concentration falls below the level at which the native state is thermodynamically unstable.
The link to join the course : Online Courses
Symptoms:
A person who has initial stage of Alzheimer, may seem healthy but has more and more trouble making sense of the world around them. They will realize gradually that something is wrong to the person and their family. Some other symptoms;
- Daily life disrupted because of memory loss
- Wrong decisions led by poor judgment
- Loss of sense of initiative and spontaneity
- Losing track of dates or knowing current location
- Taking longer to complete normal daily tasks
- Repeating questions
- Forgetting recently learned information
- Trouble paying bills and handling money
- Challenges in solving problems or planning
- Wandering and getting lost
- Losing things or misplacing them in odd places
- Difficulty completing tasks such as bathing
- Mood swings and personality changes
- Increased anxiety and aggression
Causes:
- Alzheimer’s disease is caused by the abnormal build-up of proteins in and around brain cells.
- As brain cells got affected, there’s also a decrease in chemical messengers (called neurotransmitters) that involved in sending messages, or signals, between brain cells. Levels of one neurotransmitter, acetylcholine, are particularly low in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s disease.
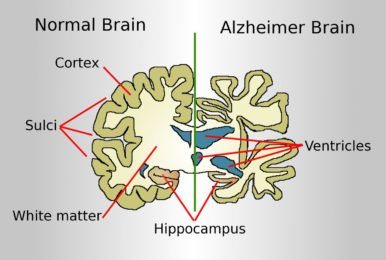
- Different areas of the brain started shrinking over the time. The first areas usually affected are responsible for memories.
- In more unusual forms of Alzheimer’s disease, different areas of the brain are affected.
- The first symptoms may be problems with vision or language rather than memory.
Factor that increase the risk:
- Age
- Age is the single most significant factor in Alzheimer. In General developing Alzheimer’s disease doubles every 5 years after you reach 65.
- But it’s not only just older people who are at risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Around 1 in 20 people with the condition are under 65.
- This is called early- or young-onset Alzheimer’s disease and it can affect people from around the age of 40.
- Family history: The genes we inherit from our parents can contribute to our risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease, although the actual increase in risk is small. But in a few families, Alzheimer’s disease is caused by the inheritance of a single gene and the risks of the condition being passed on are much higher. If several of our family members have developed dementia over the generations, and particularly at a young age. We s may want to seek genetic counselling for information and advice about our chances of developing Alzheimer’s disease when we’re older.
- Down’s syndrome : People with Down’s syndrome are at a higher risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease .This is because the genetic changes that cause Down’s syndrome can also cause amyloid plaques to build up in the brain over time, which can lead to Alzheimer’s disease in some people.
- Head injuries: People who have had a severe head injury may be at higher risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease, but much research is still needed in this area.
- Cardiovascular disease: Research shows that several lifestyle factors and conditions associated with cardiovascular disease can increase the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. These include: smoking, obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol.
Risk can be reduce by:
- Stopping smoking
- Eating a healthy taking balanced diet
- Leading an active life, both physically and mentally
- Losing weight as per BMI
- Drinking less alcohol
- Having regular health check up
Other risk factors
The latest research suggests that other factors are also important, although this does not mean these factors are directly responsible for causing dementia.
These include:
- Hearing loss
- Untreated depression (though depression can also be one of the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease)
- Loneliness or social isolation
- A sedentary lifestyle
Treatment:
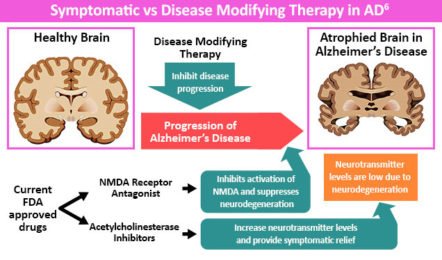
- Medications for moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease: Memantine is a medicine , scientific name; an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonist, can be prescribed for moderate to severe Alzheimer’s. This drug is prescribed to decrease symptoms, which could enable some people to maintain certain daily functions a little longer than they would without the medication. Food and drug administration(fda) approved other medicine Brexpiprazole, Donepezil, Galantamine and Rivastigmine.
- Managing behavioral symptoms
- Natural remedies for Alzheimer’s disease and other types of dementia that are based on peer-reviewed scientific evidence:
- Diet
- Exercise
- Lowering stress
- Healthy sleep
- Vitamin and nutrient supplements
- Acupuncture
- Improving heart health
- Social interaction and an active mind
- Proper oral hygiene
- Removal of environmental risk factors
Combining science-based lifestyle changes, medicinal plants, and stress reduction, our practice has seen encouraging results with many of our patients.
Best Online Coaching for Civil Service_IAS_ UPSC_IFS_IPS
Free Study Material ENSEMBLE IAS ACADEMY | Call +91 98115 06926 | Visit us:- https://ensembleias.com/ | Online Store: https://online.ensemble.net.in/
#Alzheimer #FDA #who #HEALTH #DISEASE #neurodegenrative #World_Alzheimer_day #lifestyle #medicine_sector #science_tech #current_affair #upsc_GS_paper #GSPaper3 #mcq #correct_answer #civilservicesstudy #ensembleiasacademy #geographyoptional #k_siddharthasir #strategicthinker #ias #civilservices #upsc_motivation #upsc_aspirants #upsc_exam #trendsingeography