Five Eyes- Intelligence Alliance
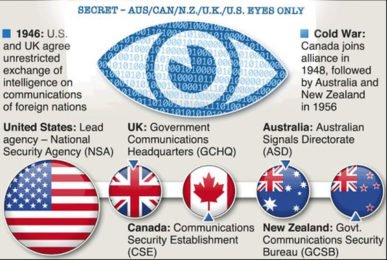
The Five Eyes an alliance was formed in 1946 (post world war-2) between five anglophone countries and their security. And the countries are;
- UNITED STATES
- U.K
- AUSTRALIA
- CANADA
- NEW ZEALAND
- It is both surveillance based and tracks signals intelligence (SIGINT).
- Intelligence documents shared between the member countries are classified ‘Secret—AUS/CAN/NZ/UK/US Eyes Only, which gave the group its title ‘Five Eyes.’
- The alliance between the U.S. and the U.K. evolved around the Second World War to counter the Cold War Soviet threat.
- The two countries, which had successfully deciphered German and Japanese codes during the war, forged a collaboration to share intelligence related to signals such as radio, satellite and internet communications.
- In 1946, the alliance was formalised through an agreement for cooperation in signals intelligence. The treaty called the British U.S.
- Communication Intelligence Agreement, or BRUSA (now known as the UKUSA Agreement), was signed between the State Army Navy Communication Intelligence Board (STANCIB) of the U.S. and the London Signal Intelligence Board (SIGINT) of Britain.
- Its scope was limited to “communication intelligence matters only” related to the “unrestricted” exchange of intelligence products in six areas: a collection of traffic; acquisition of communication documents and equipment;
- Traffic analysis; cryptanalysis; decryption and translation; and acquisition of information regarding communication organisations, practices, procedures, and equipment.
- The arrangement was later extended to ‘second party’ countries —Canada joined in 1948, while Australia and New Zealand became part of the alliance in 1956
The link to join the course : Online Courses
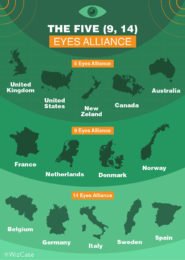
9 Eyes: Five Eyes + Denmark, France, the Netherlands and Norway.
14 Eyes: The 9 Eyes,+ Germany, Belgium, Italy, Spain and Sweden.
41 Eyes: All of the above, with the addition of the allied coalition in Afghanistan.
Tier B countries with which the Five Eyes have “focused cooperation” on computer network exploitation, including Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, Denmark, Germany, Greece, Hungry, Iceland, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, Netherland, Norway, Poland, Portugal, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and Turkey
Concern:
- There have been several concerns regarding the privacy, security and methods of working of the intelligence alliance, which remained shrouded in mystery for long.
- The alliance was embroiled in a major controversy in 2013 following the disclosure of classified documents by Edward Snowden, a former National Security Agency (NSA) contractor.
- There is no domestic legislation governing intelligence-sharing,
It means that many of these arrangements lack legal basis and therefore democratic legitimacy.
- Some of the bilateral agreements falling under the UK &USA umbrella reveal the outsourcing of espionage activities to corporations without limiting their access to classified information, contributing to the privatisation of secret service.
Solution:
- The public should have lucidity as to the circumstances in which Five Eyes intelligence agencies will share information and the procedure governing such exchange, including regulating and controlling the sharing of intelligence to what is necessary and proportionate.
- Governments must extend domestic and international limitations applicable to state inspection to international intelligence-sharing agreements to prevent the emergence of parallel surveillance frameworks with double-standards.
- In order to avoid the misdirect of intelligence information, due diligence obligations must be imposed on states obtaining, accessing, using, analysis retaining and sharing intelligence information.
- Further states must be required to analyse the accuracy or verifiability of the information received prior to acting upon it, and ensure the agencies with whom the information is shared do not have a negative human rights record.
- Oversight mechanisms must be implemented to review.
- Monitor and express recommendations on all aspects of intelligence-sharing agreements, ensuring that States comply with due diligence obligations.
Five Eyes Intelligence Alliance
Best Online Coaching for Civil Service_IAS_ UPSC_IFS_IPS
Free Study Material ENSEMBLE IAS ACADEMY | Call +91 98115 06926 | Visit us:- https://ensembleias.com/ | Online Store: https://online.ensemble.net.in/
#Five_eyes #international_relations #civil_services_study #ensemble_ias_academy #geography_optional #k_siddharthasir #ias #upsc_exam #civilservices #upsc_motivation #upsc_aspirants #trendsingeography




