Wastewater Surveillance
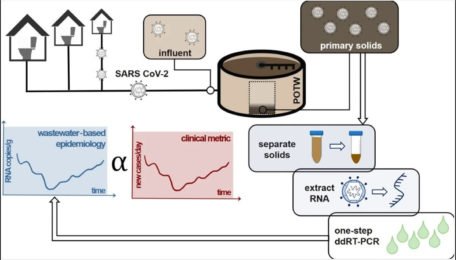
The monitoring and examination of wastewater samples in order to learn more about the presence and movement of pathogens like bacteria or viruses within a community.
It entails routinely collecting water samples and evaluating them from diverse sources, including sewage systems and wastewater ponds. The samples are then examined in special laboratories to find particular pathogen indicators or genetic fragments.
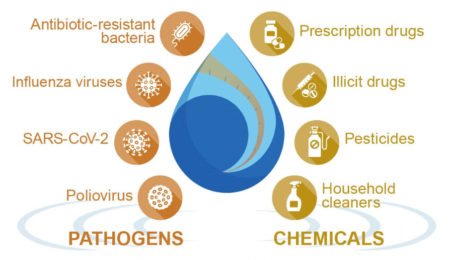
Benefits
- Before clinical cases are reported, surveillance finds disease-causing chemicals, allowing for quick action and containment measures.
- Insights into overall population health can be gained through the analysis of wastewater samples, which also helps identify illness trends and develop focused interventions.
- By removing the requirement for individual samples, wastewater surveillance lowers the cost of collection, testing, and analysis.
- Wastewater surveillance collects cases without symptoms and improves knowledge of illness prevalence, providing information beyond clinical data.
- The detection of particular genetic identifiers or pathogen pieces in wastewater samples can act as a warning sign for impending disease outbreaks.
- Prioritized resource allocation is made possible by wastewater surveillance, which tracks the occurrence of diseases in regions with poor access to healthcare services.
- Data-driven decisions for disease control, resource allocation, and targeted treatments are made possible by combining wastewater surveillance data with information from other sources.
Challenges
- India’s national public health surveillance system does not cover the entire nation equally. Rural and isolated places frequently lack the necessary surveillance infrastructure and resources, which limits their ability to gather and monitor data.
- In India, efforts to monitor diseases are frequently dispersed and narrowly focused on certain illnesses. It is challenging to identify and comprehensively respond to emerging health hazards while using this segmented approach.
- Data sharing between departments and at various levels of government in India is difficult, which impedes the smooth flow of information required for early detection and response.
- India has to make considerable improvements to its public health laboratory infrastructure and diagnostic capability. Testing can be hampered by a lack of skilled employees, old technology, and insufficient money.
- The public health monitoring system in India has major obstacles due to underreporting of diseases and variable data quality.
- India’s public health surveillance system has a limited adoption of cutting-edge technology including real-time data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence.
India Role
- Incorporating wastewater monitoring data into the current surveillance reporting systems should be a priority.
- The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission presents a chance for the integration of wastewater surveillance because it seeks to provide a seamless online platform for healthcare services.
- Public health experts should be trained in the management and analysis of data produced from wastewater surveillance in addition to established epidemiological methods.
- India has previously shown that it is dedicated to promoting resource mobilisation and public health surveillance. Political leaders must understand how wastewater surveillance may be used as a powerful instrument for disease monitoring and response.
- The vision of Niti Aayog is aligned with the integration of wastewater surveillance. To guarantee that wastewater surveillance is included in the national public health agenda, political leaders can offer strategic direction and policy assistance.
- India’s influence on global fora like the G20 offers a chance to highlight the importance of cutting edge methods of disease surveillance, such as wastewater surveillance. Political leaders can use these venues to promote improved public health surveillance and win promises and help from abroad.
- To increase funding for wastewater surveillance, political leaders might encourage public-private collaborations.
For improving disease prevention and management, the integration of wastewater surveillance into India’s public health infrastructure holds enormous promise. India has the opportunity to create a model for integrated public health surveillance that prioritises preventative measures, prompt response, and a robust healthcare system through strategic leadership.
Best Online Coaching for Civil Service_IAS_ UPSC_IFS_IPS,
Free Study Material ENSEMBLE IAS ACADEMY
Call +91 98115 06926
Visit us:- https://ensembleias.com/
Online Store: https://online.ensemble.net.in/
Email: ensembleias@gmail.com
#GS3 #GSPaper3 #SnT #Science #Technology #Wastewater #G20 #COVID #SARS #civilservicesstudy #ensembleiasacademy #geographyoptional #k_siddharthasir #strategicthinker #ias #civilservices #upsc_motivation #upsc_aspirants #upsc_exam #trendsingeography #trendofquestions #geographytrends




