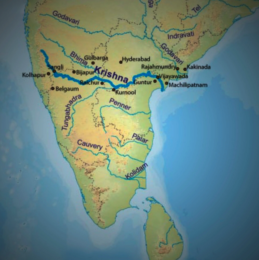
Krishna River is one of the longest rivers of India (about 1300 km in length). It originates at Mahabaleswar in Maharashtra, passes through Sangli and meets the sea in the Bay of Bengal at Hamasaladeevi in Andhra Pradesh. The Krishna River flows through the states of Maharashtra, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh. Krishna River System is thus formed.
Also Read : Indian Drainage System
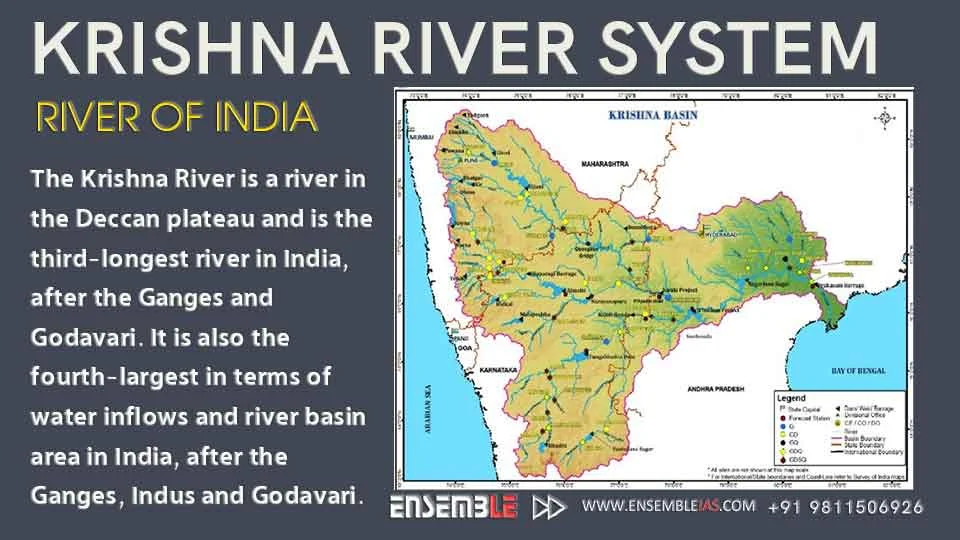
The Krishna River is a river in the Deccan plateau and is the third-longest river in India, after the Ganges and Godavari. It is also the fourth-largest in terms of water inflows and river basin area in India, after the Ganges, Indus and Godavari.
The traditional source of the river is a spout from the mouth of a statue of a cow in the ancient temple of Mahadev in Mahabaleshwar.
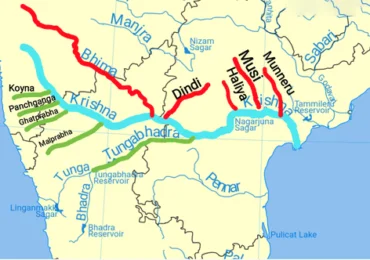
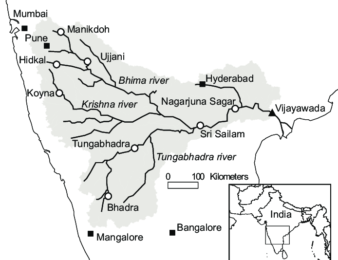
Its most important tributary is the Tungabhadra River, which itself is formed by the Tunga and Bhadra rivers that originate in the Western Ghats. Other tributaries include the Koyna, Bhima, Mallaprabha, Ghataprabha, Yerla, Warna, Dindi, Musi and Dudhganga rivers.
Length: 1,400 km
Discharge: 1,642 m³/s
Basin area: 258,948 km²
Source: Mahabaleshwar
Mouths: Bay of Bengal, Hamsaladeevi
Cities: Vijayawada, Sangli
Islands: Bhavani Island
To buy our online courses: Click Here
The Krishna Basin in the Krishna River System extends over Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra and Karnataka having a total area of 2,58,948 Sq.km which is nearly 8% of the total geographical area of the country. The basin has a maximum length and width of about 701 km and 672 km and lies between 73°17’ to 81°9’ east longitudes and 13°10’ to 19°22’ north latitudes. It is bounded by Balaghat range on the north, by the Eastern Ghats on the south and the east and by the Western Ghats on the west. The Krishna River rises from the Western Ghats near Jor village of Satara district of Maharashtra at an altitude of 1,337 m just north of Mahabaleshwar.
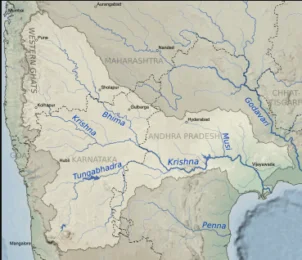
The total length of river from origin to its outfall into the Bay of Bengal is 1,400 km. Its principal tributaries joining from right are the Ghatprabha, the Malprabha and the Tungabhadra whereas those joining from left are the Bhima, the Musi and the Munneru are joining the river from left. The major part of basin is covered with agricultural land accounting to 75.86% of the total area and 4.07% of the basin is covered by water bodies. The basin spreads over 56 parliamentary constituencies (2009) comprising 23 of Andhra Pradesh, 18 of Karnataka, and 15 of Maharashtra.
For more details : Best Online Coaching for Civil Service_IAS_ UPSC_IFS_IPS,
Free Study Material ENSEMBLE IAS ACADEMY
Call +91 98115 06926
Be a contributor, write articles:- Unleash the writer within you
Online Store: https://online.ensemble.net.in/
Email: ensembleias@gmail.com