Write the correct answer
Correct statement about Nipah Virus
- It is Plant pathogen Virus.
- A Bat borne Zoonotic virus .
- A fruit Petropodidea family are the natural host of Nipah Virus.
- No vaccine or medicine available for animal and people.
- Nipah virus infection Symptomatic disease in Human.
- Only b
- Only a,c,e
- Only b,c,d
- Only c,d
The link to join the course : Online Courses
Correct Answer :
Ans: 3 (b,c,d) are the correct statement
Explanation:
- Statement B is correct; Nipah virus (NiV) is a zoonotic virus (it is transmitted from animals to humans) and can also be transmitted through contaminated food or directly between people.
- Nipah virus in pigs and other domestic animals such as horses, goats, sheep, cats and dogs were first reported during the initial Malaysian outbreak in 1999.
- The virus is highly contagious in pigs. Pigs are infectious during the incubation period, which lasts from 4 to 14 days
- Transmission: During the first recognized outbreak in Malaysia, which also affected Singapore, most human infections resulted from direct contact with sick pigs or their contaminated tissues. Transmission is thought to have occurred via unprotected exposure to secretions from the pigs, or unprotected contact with the tissue of a sick animal.
- In subsequent outbreaks in Bangladesh and India, consumption of fruits or fruit products (such as raw date palm juice) contaminated with urine or saliva from infected fruit bats was the most likely source of infection.
- There are currently no studies on viral persistence in bodily fluids or the environment including fruits.
- Human-to-human transmission of Nipah virus has also been reported among family and care givers of infected patients.
Prevention and Reducing the risk of infection in people
- Controlling Nipah virus in pigs
- Currently, there are no vaccines available against Nipah virus. Based on the experience gained during the outbreak of Nipah involving pig farms in 1999, routine and thorough cleaning and disinfection of pig farms with appropriate detergents may be effective in preventing infection.
- If an outbreak is suspected, the animal premises should be quarantined immediately. Culling of infected animals – with close supervision of burial or incineration of carcasses – may be necessary to reduce the risk of transmission to people. Restricting or banning the movement of animals from infected farms to other areas can reduce the spread of the disease.
- As Nipah virus outbreaks have involved pigs and/or fruit bats, establishing an animal health/wildlife surveillance system, using a One Health approach, to detect Nipah cases is essential in providing early warning for veterinary and human public health authorities.
- In the absence of a vaccine, the only way to reduce or prevent infection in people is-
- a) by raising awareness of the risk factors and
- b) educating people about the measures they can take to reduce exposure to the Nipah virus.
- Reducing the risk of bat-to-human transmission.
- a) focus on decreasing bat access to date palm sap and other fresh food products.
b)Keeping bats away from sap collection sites with protective coverings (such as bamboo sap skirts) may be helpful.
c)Freshly collected date palm juice should be boiled, and fruits should be thoroughly washed and peeled before consumption. Fruits with sign of bat bites should be discarded.
- Reducing the risk of animal-to-human transmission.
a)Gloves and other protective clothing should be worn while handling sick animals or their tissues, and during slaughtering and culling procedures.
- b) As much as possible, people should avoid being in contact with infected pigs. In endemic areas, when establishing new pig farms, considerations should be given to presence of fruit bats in the area and in general, pig feed and pig shed should be protected against bats when feasible.
- Reducing the risk of human-to-human transmission.
- a) Close unprotected physical contact with Nipah virus-infected people should be avoided.
- b) Regular hand washing should be carried out after caring for or visiting sick people.
- Controlling infection in health-care settings
a)Health-care workers caring for patients with suspected or confirmed infection, or handling specimens from them, should implement standard infection control precautions at all times.
b)As human-to-human transmission has been reported, in particular in health-care settings, contact and droplet precautions should be used in addition to standard precautions. Airborne precautions may be required in certain circumstances.
- c) Samples taken from people and animals with suspected Nipah virus infection should be handled by trained staff working in suitably equipped laboratories.
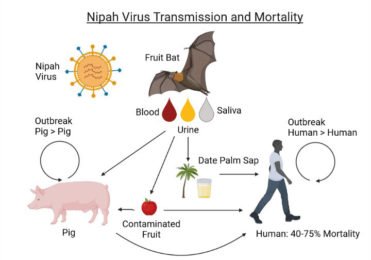
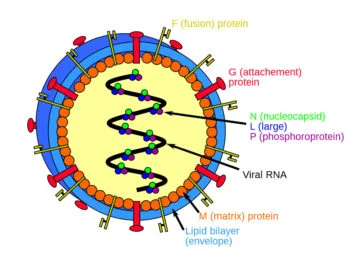
- Statement C is correct; Fruit bats of the family Pteropodidae– particularly species belonging to the Pteropus genus – are the natural hosts for Nipah virus. There is no apparent disease in fruit bats. African fruit bats of the genus Eidolon, family Pteropodidae, were found positive for antibodies against Nipah and Hendra viruses, indicating that these viruses might be present within the geographic distribution of Pteropodidae bats in Africa.
- Statement D is correct; as per WHO, there are no vaccines available against Nipah virus.
- Nipah virus infection in humans causes a range of clinical presentations, from asymptomatic infection (subclinical) to acute respiratory infection and fatal encephalitis.
Best Online Coaching for Civil Service_IAS_ UPSC_IFS_IPS
Free Study Material ENSEMBLE IAS ACADEMY | Call +91 98115 06926 | Visit us:- https://ensembleias.com/ | Online Store: https://online.ensemble.net.in/
#mcq #correct_answer #civilservicesstudy #ensembleiasacademy #geographyoptional #k_siddharthasir #strategicthinker #ias #civilservices #upsc_motivation #upsc_aspirants #upsc_exam #trendsingeography




